Carbon Capture and Underground Storage (CCUS) - Toshiba use case
- Angel Solutions (SDG)

- Jun 4, 2024
- 1 min read
Updated: Jul 20, 2024
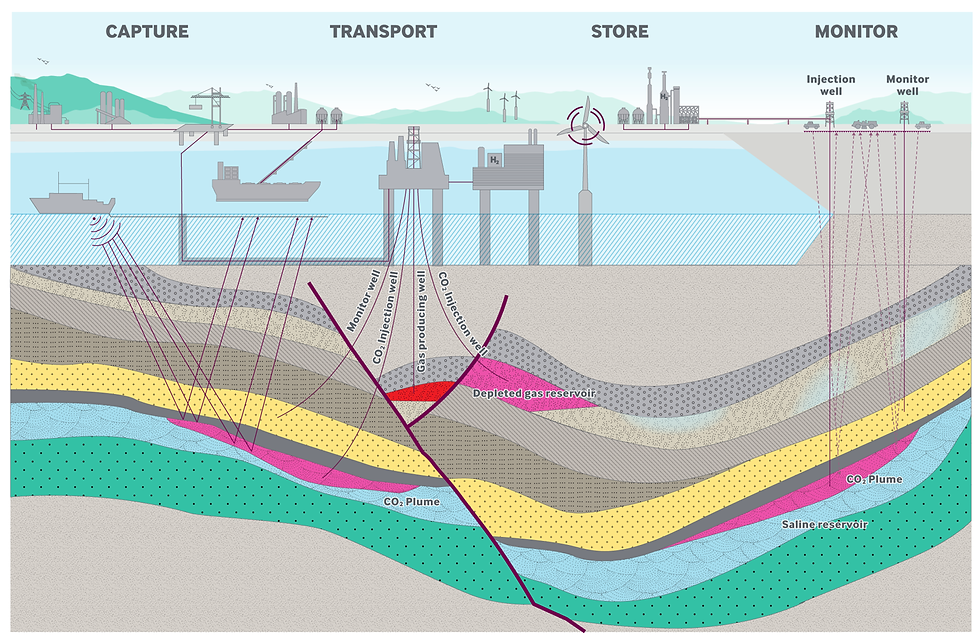
Carbon Capture and Underground Storage (CCUS) includes technologies that decrease carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from large point sources or remove CO2 from the atmosphere. The captured CO2 is stored in carefully chosen and monitored underground locations, such as depleted oil reservoirs. CCUS plays a crucial role in helping to achieve global climate targets.

The image below illustrates schematically how CCUS works:
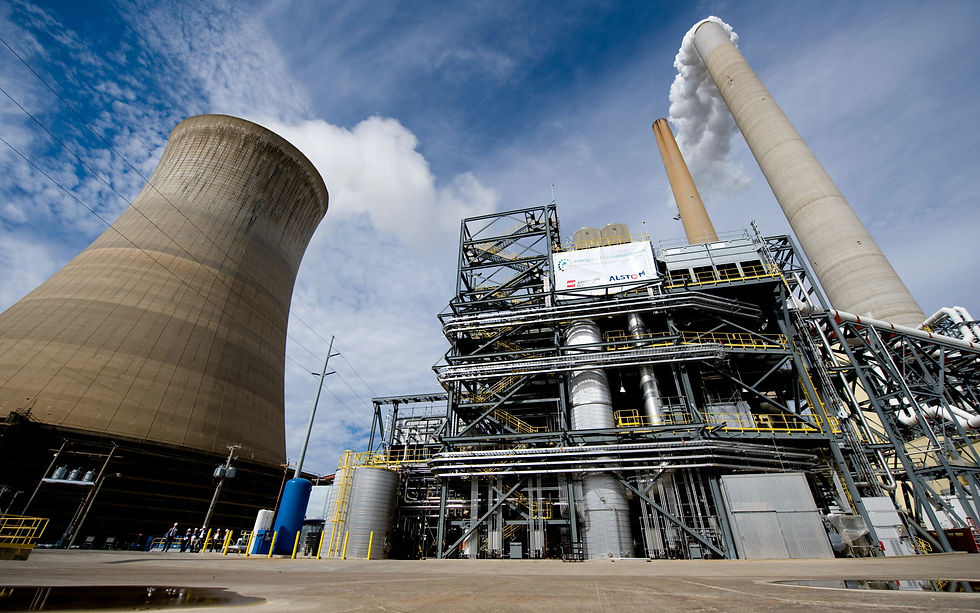
Toshiba Energy Systems and Solutions Corporation has started operating a large-scale carbon capture facility at the Mikawa Power Plant in Omuta, Fukuoka prefecture. The plant has a capacity of 50,000 kW. This is part of the “Demonstration of Sustainable CCUS Technology Project” sponsored by Japan’s Ministry of the Environment (MOE) and involves 18 entities, including Toshiba ESS.

In light of these circumstances, Toshiba ESS is actively championing the adoption of CO2 capture and underground storage technology while delivering highly efficient and environmentally friendly power generation equipment and services.
Takao Konishi, Director and Senior Vice-President of Power Systems Division at Toshiba ESS commented, “We are honored to start the operation of this large-scale carbon capture facility. Through this project, we will contribute to the global promotion of cleaner energy production by developing and deploying CO2 capture technology, including its application to biomass power plants.”
Here you can access additional resources on this topic and related subjects, and also here. Please don't hesitate to contact us if you need any further assistance. And visit our YouTube Channel and subscribe.



Comments